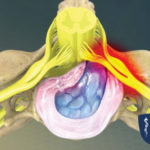
The discs located between vertebrae create and form the spine, allow for movement and absorb weight placed on the spine. Discs are made up of a tough outer layer and a gel-like inner layer. When a disc is compressed, pressure builds up in the inner layer, causing the disc to bulge. Most bulging discs happen in the lower back, but at times they can be found in the neck and upper back also. However, about 52% of those with bulging discs experience no symptoms or pain.
A physician can diagnose a bulging disc or discs with the results from a MRI or CT scan. If you have experienced 4-6 weeks of severe pain or have not seen results from conservative therapies, diagnostic imaging is suggested. These results can also help determine the cause of the pain. Most bulging discs will heal within a month when treated conservatively and will not require surgical care.
Treating this condition may involve rest, physical therapy to build strength and stability, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory or pain relief medications (NSAIDs). If necessary, the doctor may order a steroid injection to reduce inflammation or prescribe a prescription-strength opiate medication.
Schedule your appointment today and meet with our providers to discover if this treatment is right for you.